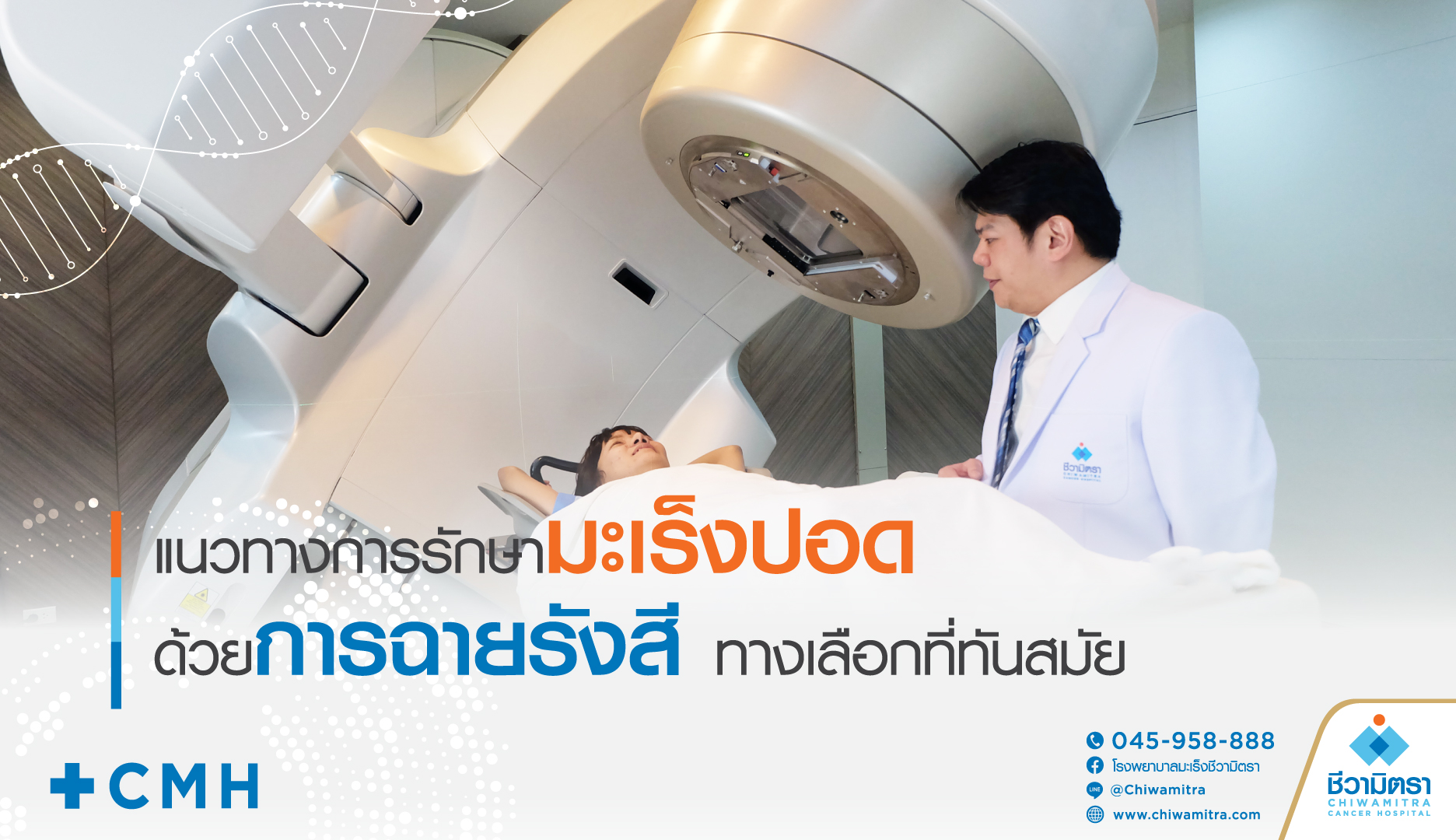
In an era of rapid medical advancements, radiation therapy has become a modern and highly effective treatment option for lung cancer patients. Radiation is a process that uses high-energy beams to destroy or inhibit the growth of cancer cells, specifically targeting the tumor while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Radiation Therapy Approaches for Lung Cancer
Radiation therapy is a crucial treatment for controlling the growth of cancer cells, especially for tumors that are inoperable or unresponsive to other treatments. For non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in particular, radiation is beneficial for reducing tumor size and alleviating symptoms caused by the cancer’s spread.
Types of Radiation Therapy for Lung Cancer
There are three main types of radiation therapy used to treat lung cancer:
External Beam Radiation Therapy: This approach uses a machine located outside the body to deliver radiation beams to the tumor site. The machine works with precise imaging technology to pinpoint the exact location of the cancer. This method is suitable for treating lung cancer that has not spread or is inoperable, with various techniques such as 3D-CRT and SBRT available.
Brachytherapy: Also known as internal radiation therapy, brachytherapy involves placing a radioactive source directly inside or near the cancer. This allows the radiation to be concentrated on the tumor, reducing the risk of affecting nearby tissues. This method is often used for small tumors within the lung or those that are difficult to access with other techniques.
Proton Therapy: This advanced therapy uses high-energy proton particles to destroy cancer cells. A key advantage of proton therapy is its ability to precisely target the tumor without significantly affecting surrounding healthy tissues, making the treatment safer with fewer side effects compared to conventional radiation.
Benefits of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy for lung cancer offers several advantages:
High Precision: The treatment directly targets cancer cells without causing excessive damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Fewer Side Effects: Compared to other treatments like surgery or chemotherapy, radiation therapy often has fewer and more manageable side effects.
Who is a Suitable Candidate for Radiation Therapy?
Radiation therapy is an ideal option for patients who:
Cannot Undergo Surgery: Patients who are unable or unwilling to have surgery can choose radiation as an alternative.
Have High Surgical Risk: This includes patients with other medical conditions that make surgery unsafe.
Cannot Tolerate Anesthesia: Patients with health issues that prevent them from tolerating anesthesia or surgery.
Radiation therapy is a precise and low-risk treatment option for lung cancer, especially for patients who cannot undergo surgery. It can effectively shrink tumors and improve treatment outcomes, particularly in cases where the cancer is in an inoperable stage.